Complete Protein Combinations Chart for Vegans

What are complete proteins?
Complete proteins are a type of protein that contains all nine essential amino acids that the human body needs. These amino acids cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through the diet. Take a look at the complete protein combinations chart to see how you can match each protein for your vegan diet.
Consuming complete proteins is important for maintaining good health and supporting the body’s various functions. Protein is a vital nutrient that plays a role in the growth and repair of tissues, the production of enzymes and hormones, and the transportation of nutrients throughout the body. It is also necessary for building and repairing muscle tissue, which is important for maintaining strength and physical function.
While it is important to consume adequate amounts of protein, it is also important to choose sources of protein that are nutrient-dense and not high in saturated fat and other unhealthy additives. It is generally recommended to focus on plant-based sources of protein, such as beans, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Why are complete proteins important?
Complete proteins are important for maintaining good health and supporting the body’s various functions. When the body does not have access to all of the essential amino acids that it needs, it can lead to a deficiency in one or more of these amino acids. This can have negative effects on health, including decreased muscle mass, impaired immune function, and reduced healing and repair of tissues.
In addition to providing the body with all of the essential amino acids, complete proteins also contain other important nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals. These nutrients are necessary for various bodily processes and help to support overall health and well-being.
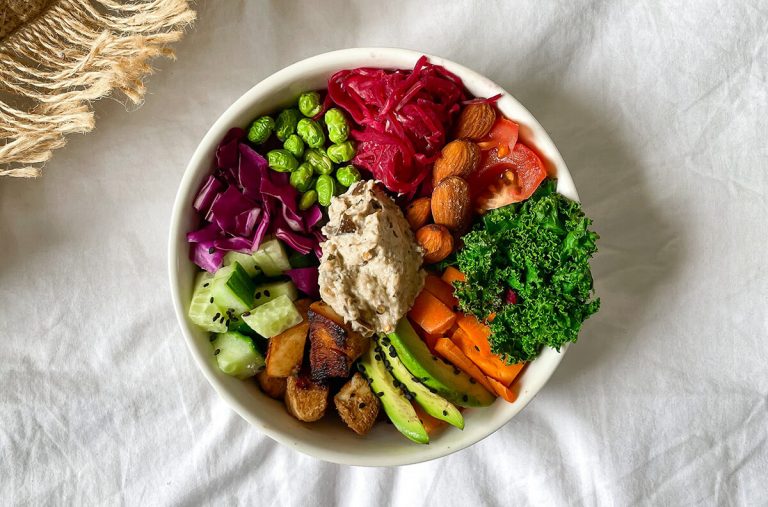

Which foods are complete proteins?
Which foods are plant-based complete proteins for vegans?
- Legumes
- Beans
- Soy
- Quinoa
- Chia Seeds
- Hemp Seeds
- Nuts
- Whole Grain
- Buckwheat
- Amaranth
- Spirulina
Legumes
Legumes are a type of plant-based food that are high in protein and contain all nine essential amino acids, making them a complete protein source for vegans. Legumes include beans, lentils, peas, and peanuts, and they are a staple in many vegan diets. In addition to their high protein content, legumes are also a good source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them a nutritious choice for vegans and non-vegans alike. Legumes can be enjoyed in a variety of dishes, such as soups, stews, salads, and dips, and can be a great way to add protein and other nutrients to a vegan diet.
Beans
Beans are a staple in many vegan diets and are a good source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. There are many different types of beans to choose from, including kidney beans, black beans, navy beans, and lentils, each of which has a unique flavor and texture. Beans can be enjoyed in a variety of dishes, such as soups, stews, salads, and dips, and can be a great way to add protein and other nutrients to your vegan diet.
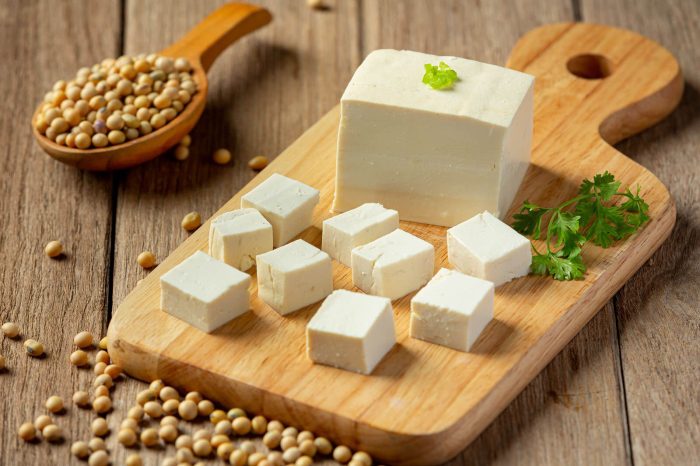
Soy

Quinoa
Quinoa is a grain that is high in protein and contains all nine essential amino acids. It is also a good source of fiber, iron, and other nutrients.
Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are a good source of complete protein and contain all nine essential amino acids. They are also high in fiber and other nutrients.
Hemp Seeds
Hemp seeds are a good source of complete protein and contain all nine essential amino acids. They are also high in omega-3 fatty acids and other nutrients.
Nuts
Nuts are a good source of protein and contain a variety of essential nutrients, such as healthy fats, fiber, and vitamins and minerals. Some examples of nuts that are high in protein and can be included in your diet include almonds, peanuts, and cashews. Nuts can be enjoyed as a snack on their own or added to a variety of dishes, such as salads, grain bowls, and baked goods, for a boost of protein and other nutrients.
Whole Grain
Whole grains are a good source of protein and contain a variety of essential nutrients, such as fiber, B vitamins, and minerals. Some examples of whole grains that are high in protein and can be included in a vegan diet include quinoa, amaranth, and buckwheat. Whole grains can be enjoyed in a variety of dishes, such as bowls, salads, and soups, or used as a base for a vegan protein-rich meal.
Buckwheat
Buckwheat is another grain that is high in protein and contains all nine essential amino acids. It is also a good source of fiber and other nutrients.
Amaranth
Amaranth is a grain that is high in protein and contains all nine essential amino acids. It is also a good source of fiber and other nutrients.
Spirulina
Spirulina is a type of blue-green algae that is high in protein and contains all nine essential amino acids. It is also a good source of antioxidants and other nutrients.
Complete Protein Combination Vegan Chart:
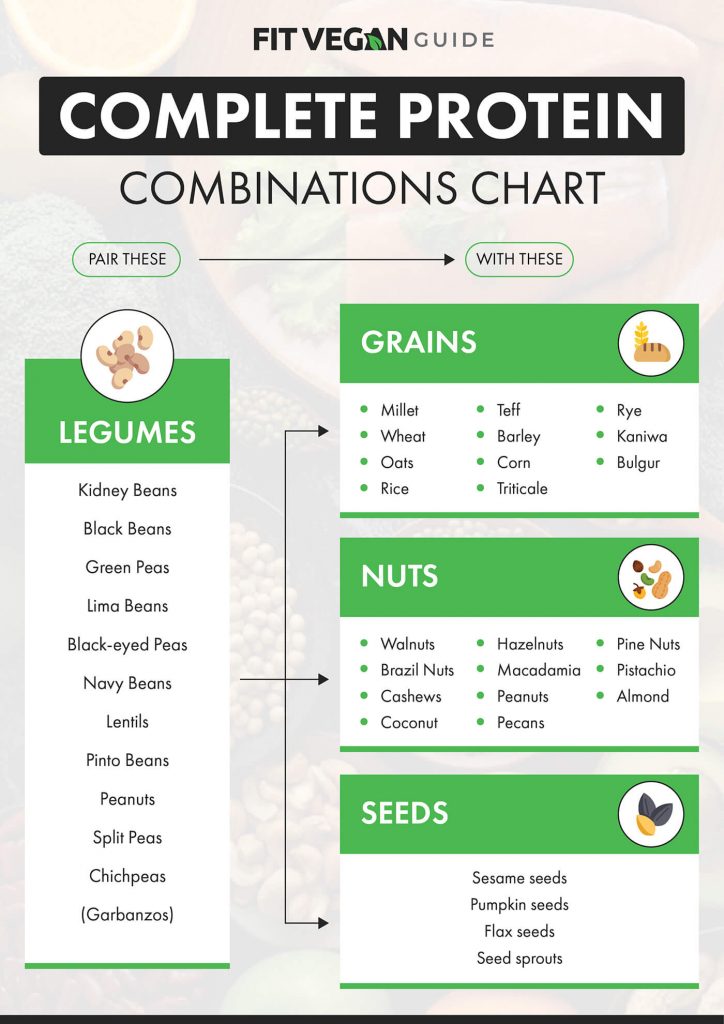
How much protein do you need?
The recommended daily protein intake varies on a few factors. These include your age, sex, and level of physical activity. In general, it is recommended that adults consume at least 0.36 grams of protein per pound of body weight per day. Vegan diets tend to require more because plant-based proteins can be harder for the body to absorb. On average, most vegan adults should have about 0.9 – 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight every day for optimal health.
However, these recommendations can vary based on a person’s individual needs and circumstances. For example, athletes and people who engage in regular, intense physical activity may have higher protein needs due to the increased demand on their muscles. You can use this calculator to figure out how much protein you need.
It is important to consume an appropriate amount of protein to support good health and well-being. In addition to supporting muscle growth and repair, protein also plays a role in the production of enzymes and hormones, and the transportation of nutrients throughout the body. By consuming a variety of protein-rich foods, including both complete and incomplete proteins, individuals can meet their protein needs and support good health.
What is the difference between complete and incomplete proteins?
Complete proteins are a type of protein that contains all nine essential amino acids that the human body needs. These amino acids cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through the diet. Complete proteins are typically found in animal-derived foods, such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products, as well as some plant-based sources, such as quinoa, buckwheat, and soy.
Incomplete proteins, on the other hand, are those that do not contain all nine essential amino acids. They may need to be combined with other protein sources in order to provide the body with all of the necessary amino acids. Incomplete proteins are found in a variety of plant-based foods, such as grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Complete Protein Combinations Ideas and Examples
This combination is often referred to as a “complete protein pair” and is popular in many vegetarian and vegan diets. It is also a staple in many traditional cuisines around the world, such as Latin American, Caribbean, and Asian cultures.
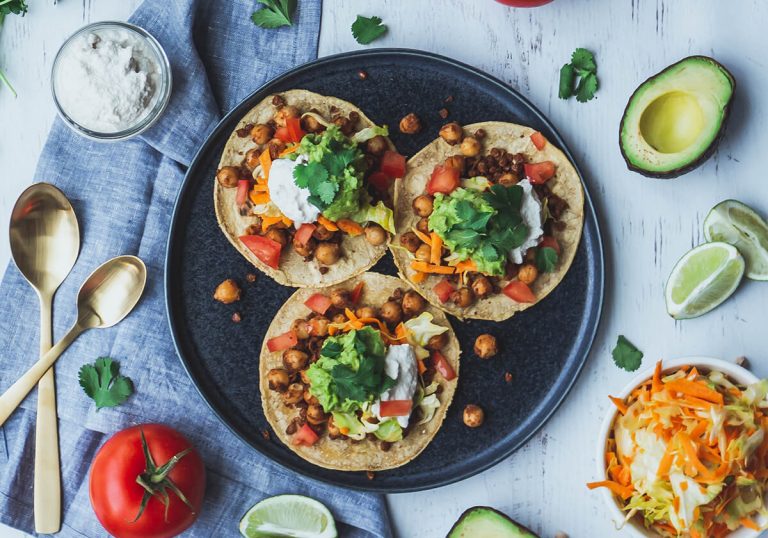

Complete protein combinations:
Rice and Beans
Beans and rice are both good sources of protein and can be combined to create a complete protein. Beans are a type of legume that are high in protein. Rice is a type of grain that is lower in protein and is considered an incomplete protein. However, when beans and rice are consumed together, they can provide the body with all nine essential amino acids and create a complete protein.
Peanut Butter Sandwich
Peanut butter is a good source of protein and contains all nine essential amino acids. Whole grain bread is an incomplete protein, but when combined with peanut butter, the two create a complete protein.
Bean Soup and Crackers
Beans, such as kidney beans, black beans, and lentils, are a complete protein on their own. Crackers are usually made from grains, such as wheat, corn, or rice, and are considered an incomplete protein. However, when combined with beans in a soup, the two create a complete protein.
Pasta and Peas
Pasta is made from grains, typically wheat, and is a good source of carbohydrates and a small amount of protein. A 1-cup serving of cooked pasta contains about 7 grams of protein. Peas, on the other hand, are a good source of plant-based protein. A 1-cup serving of cooked peas contains about 8 grams of protein. Together, pasta and peas can provide a good balance of carbohydrates and protein.
Noodles with Peanuts Combination
Pasta is usually made from grains, such as wheat, corn, or rice, and is considered an incomplete protein. Peas, on the other hand, are a complete protein.
Pita Bread and Hummus
Hummus is made from chickpeas, which are a complete protein, and contains all nine essential amino acids. Pita bread is an incomplete protein, but when combined with hummus, the two create a complete protein.
Barley and Lentil Soup
Barley and lentil soup is an excellent vegan combination for anyone looking to get a complete protein in their meal. Both barley and lentils contain all the essential amino acids you need, making them a great vegan source of proteins that are also full of fiber and many other vital nutrients. This vegan soup adds variety to the vegan menu, and makes achieving your daily protein intake goal easier than ever. Combined with some roasted vegetables or a fresh green salad, this vegan friendly soup makes a tasty, complete meal that provides plenty of nutrition.
Whole Wheat Bread with Peanut Butter
Peanut butter is a good source of plant-based protein, and when paired with whole wheat bread. In addition to being a good source of protein, peanut butter is also a good source of healthy fats, fiber, and several important nutrients, including vitamin E, magnesium, and potassium. Whole wheat bread and peanut butter is a nutritious and satisfying combination.
Busting Myths
It’s time to bust some myths and reveal how a plant-based diet provides all the essential amino acids your body needs.
Debunking the Complete Protein Myth
The myth that vegans can’t get complete proteins is just that—a myth. Every essential amino acid can be sourced from plants, and you don’t need to stress about combining foods at every meal to get your full quota. Let’s set the record straight and embrace the power of plant-based eating.
Soy as a Protein Source
Despite misconceptions, soy is a complete, healthful protein source for vegans. It’s important to understand that soy’s bad reputation is unfounded, and it can be a beneficial part of your diet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what makes a complete protein is important for vegans who want to ensure they get enough essential amino acids from their diets without having to rely on animal products. While it might require a little bit more planning than omnivorous diets do, there are plenty of alternatives available.
Soy products like tofu, tempeh, edamame beans and soymilk are all good sources of complete protein. Quinoa is another popular choice because it contains all nine essential amino acids in addition to being rich in other vitamins and minerals like iron and magnesium. Nuts like almonds or cashews also make great snacks that provide complete protein; mix them with dried fruits for an even bigger nutritional boost! And don’t forget about legumes like lentils–they’re packed with plant-based protein plus fiber to keep you full longer!
These are some foods that can provide a vegan with all nine essential amino acids necessary for optimal health! With these tips in mind you’ll be sure to have no problem getting enough complete proteins into your diet!






I would like to use your protein complementing chart in my soon to be published book, Organic Cooking for (not so organic) Families. How may I do so?
Marlene Bumgarner
Thanks for reaching out! Please just credit back to our website 🙂